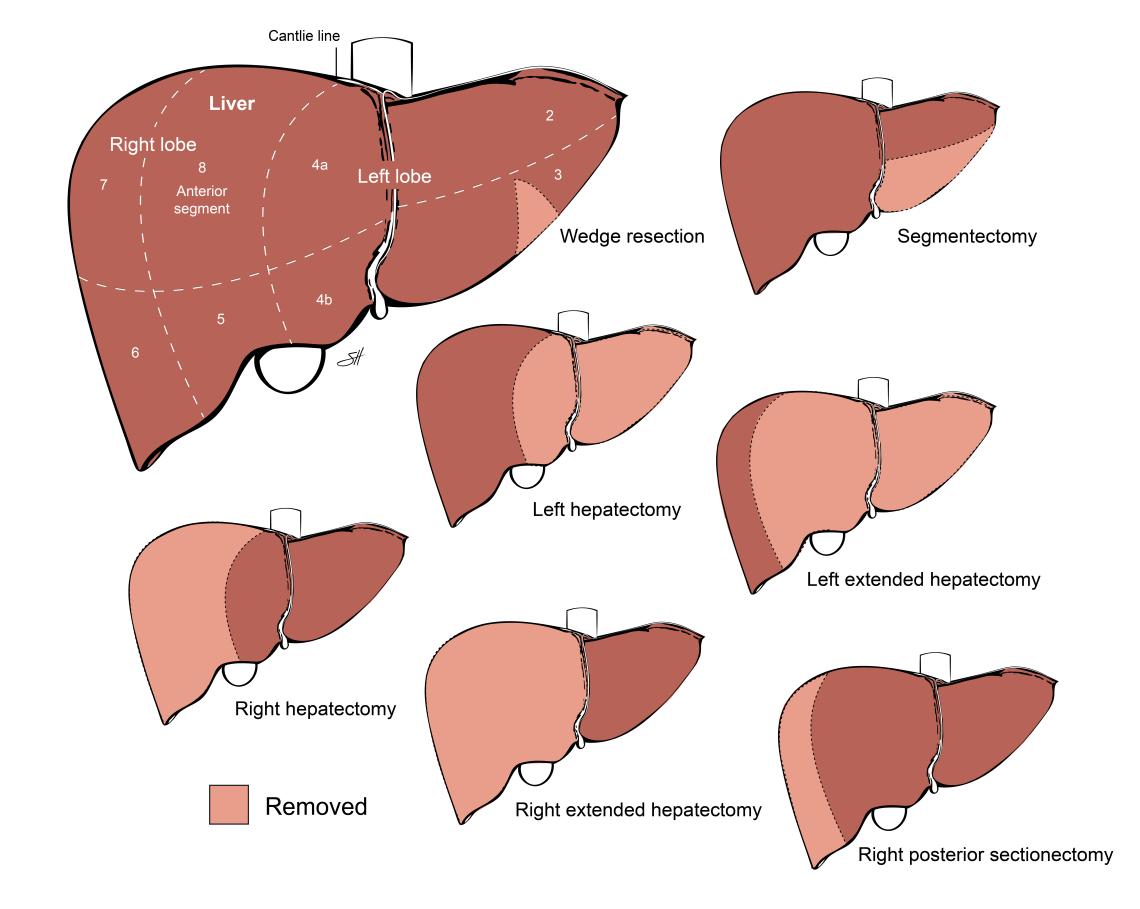
What Is a Liver Resection?
Liver resection is a surgical procedure to remove part of the liver.
When Is Liver Resection Recommended?
Liver resection is recommended to treat some types of cancer originating in the liver (hepatocellular cancer, bile duct cancer, and gallbladder cancer), and occasionally benign liver tumors that are causing pain or other problems. It may also be recommended to treat certain cases of cancer that started in other organs that have metastasized or spread to the liver (colorectal cancer, breast cancer, sarcomas, neuroendocrine cancers, and some other types).
The procedure removes the part of the liver with the tumor and some of the healthy liver tissue around it. This helps to keep the cancer from spreading to other parts of the body.
Up to three quarters of the liver can be removed as long as the rest is healthy and can continue performing normal liver functions, which are essential for life. If the liver is not healthy, such as cirrhosis from hepatitis B or C virus infection, less liver can be removed safely.
What to Expect
Sometimes, liver resection can eliminate all the cancer from the liver. But even when the procedure cannot remove all the cancer, it can help people live longer. Sometimes it is possible to remove the larger tumors in the liver and kill any smaller remaining tumors with techniques that heat the tumor, like radiofrequency or microwave ablation.
About half of the people who have the procedure are still alive five years after the surgery.
- Liver resection requires hospitalization.
- Liver resection requires general anesthesia.
- The surgery can take two to five hours.
- After surgery, the patient may stay in the hospital for five to seven days, or as long as two weeks.
- Chemotherapy and radiation therapy may be needed after liver resection.
When Is Liver Resection Not Recommended?
Patients are followed closely for many years after removal of any type of cancerous liver tumor to be certain no new tumors appear. There can be microscopic cancer cells in the liver or other organs that cannot be detected at the time of the liver resection, so we watch with blood tests and scans every four to six months to see if tumors grow to a size we can detect.
Liver resection is not recommended to treat liver cancer when:
- The cancer is large and near major blood vessels or bile ducts in the liver.
- The cancer is in many parts of the liver.
- The cancer has spread beyond the liver.
- The cancer is located right on the major vein bringing blood into the liver (portal vein), but tumors can be removed if located only on the left or right branch of the portal vein in the liver.
- People with liver cancer also have other liver diseases, such as cirrhosis.
Risks and Side Effects of Liver Resection
Possible complications of liver resection include:
- Bleeding
- Infection
- Scar tissue from the surgery
- Jaundice (eyes and skin turn yellow, usually temporary)
References
National Cancer Institute, Adult Primary Liver Cancer Treatment
American Cancer Society, Liver cancer surgery








 Credit
Credit