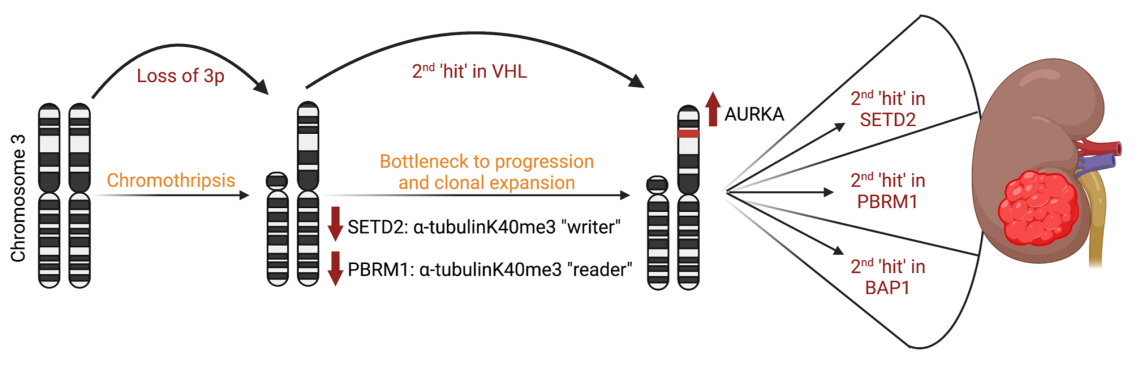
Tumor Suppressors Loss
The Dere Lab is actively working on understanding and evaluating the crosstalk between tumor suppressors lost as part of chromosome 3p deletion associated with renal cell carcinoma (RCC). Clear cell renal cell carcinoma (ccRCC) epitomizes a heterogenous cancer with multiple drivers of tumorigenesis where deletion of the short arm of chromosome 3, results in the loss of the von Hippel Lindau (VHL) tumor suppressor and several chromatin remodelers including Set-domain containing 2 (SETD2), polybromo-1 (PBRM1) and BRCA-associated protein 1 (BAP1). Although 3p deletion is the initiating driver of malignancy, the crosstalk between these tumor suppressors remains unexplored, in the context of a recent paradigm shift identifying non-chromatin functions for these traditionally nuclear enzymes.
The lab utilizes innovative biochemical assays, cutting-edge microscopy, and gene editing technologies in human and mouse models to characterize the crosstalk and evaluate phenotypic consequences resulting from disruption or loss of single or combinatorial chromatin modifiers.
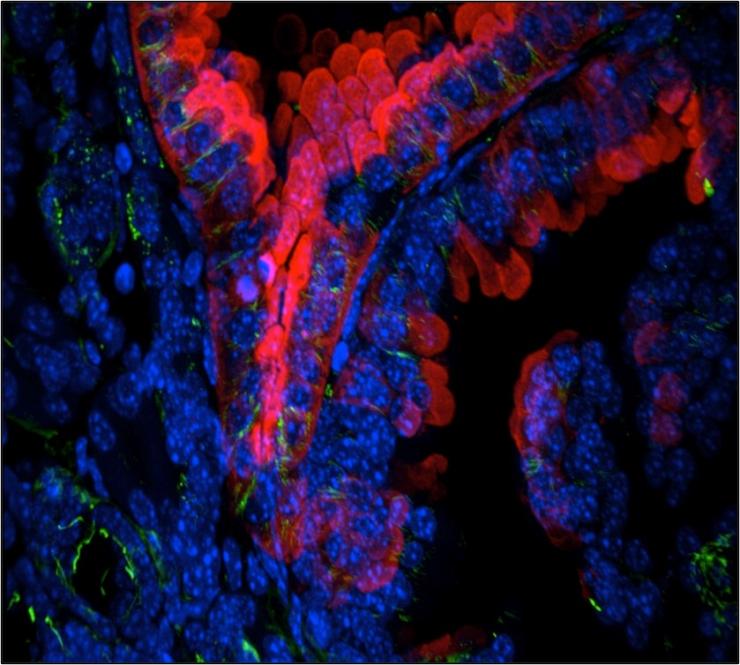
Localization of the Chromatin Modifiers Lost in RCC at the Mitotic Spindle
Recent work from our lab and others have localized the chromatin modifiers lost in RCC at the mitotic spindle. This unique convergence of RCC tumor suppressors on the cytoskeleton evokes questions about their role and regulation in a highly dynamic and critical cellular process. ccRCC has been traditionally viewed as a slow growing, long latency tumor with a low mitotic index.
Consequently, mitosis-related defects have been overlooked as therapeutic targets in this disease. However, could the novel functions of these enzymes during mitosis contribute to our understanding of early initiating events in RCC and identify the existence of compensatory mechanisms and shed light on novel therapeutic targets?
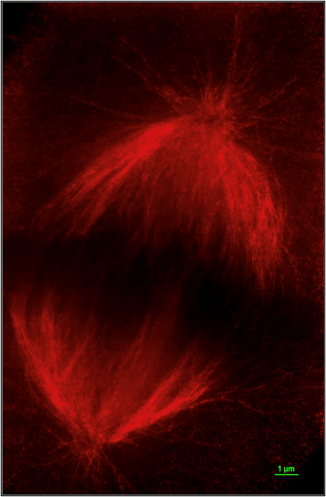
Remodeling/Reshaping of the Cytoskeleton
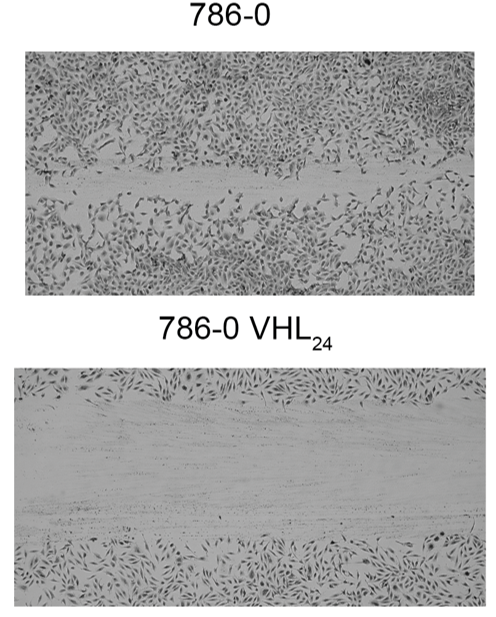
The cytoskeleton is a complex network of filaments contributing to cellular shape and required for the transport of key cellular components involved in multiple processes including cell division. The dynamic remodeling/reshaping of the cytoskeleton is critical in normal cells and disruption is often associated with increased genomic instability, enhanced migration, and motility and ultimately tumor growth and invasiveness. Chromatin modifiers such as SETD2 methylate microtubules and actin.
What are the phenotypic consequences of modulating PTMs on the cytoskeleton, how do they contribute to genomic instability and ultimately oncogenesis?
Can we gain insights into processes impacted by disruption of the cellular cytoskeleton?








