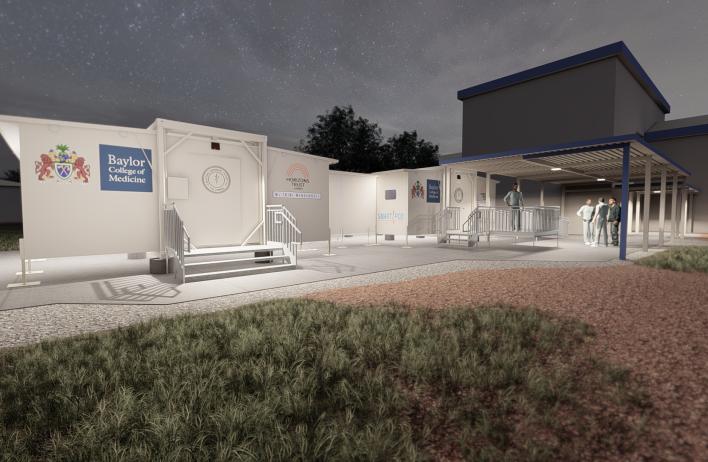
Spotlight: Smart Pod®
Designed in the wake of the 2014 Ebola outbreak, the Smart Pod is a deployable field hospital with all of the advantages of a modern hospital. Smart Pods provide a solution for areas of the world that have enormous challenges and limitations in accessing healthcare.
They can serve as primary care clinics, surgery centers, hospitals, and laboratory facilities or be easily and quickly transported anywhere in the world for an immediate response to global disasters.
Each pod can be shipped directly to its destination by boat, truck or air, and assembled in less than five minutes with a team of four. The structures are lightweight and eco-friendly, and can be customized for integration into various cultural communities.
Medical equipment and supplies are shipped in the interior of the unit, which is the footprint of a 8’ x 20’ shipping container. Once the container reaches its destination, it is quickly setup in minutes and expands to over 400 square feet. Custom features are also available.
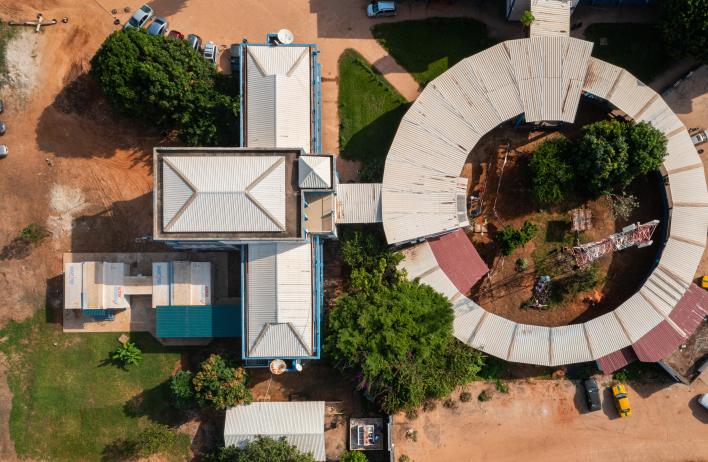


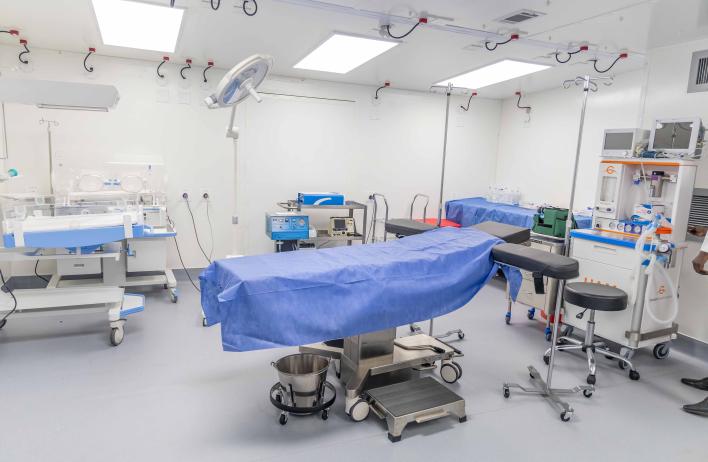
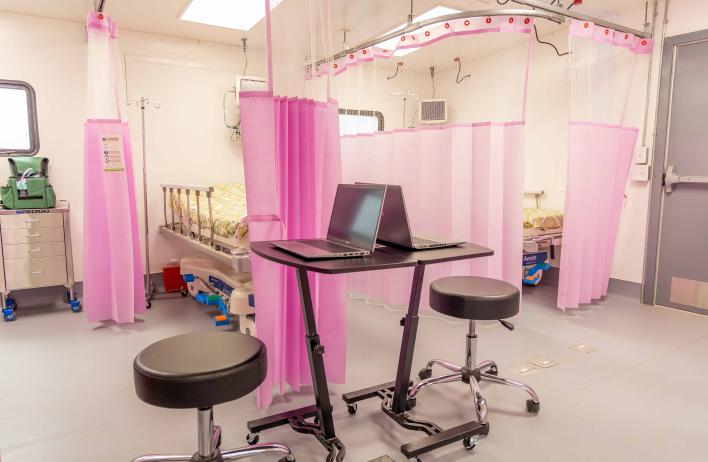
Global Portability
- ISO-standard shipping container: transported anywhere globally by ship, train, truck or helicopter
- Deployed and expanded on most surfaces with as few as 4 people in < 20 minutes
Innovation
- Designed by clinicians, for clinicians; validated by NASA engineers
- ~400 sq. footprint of usable space; 2.5x more capacity than 20-ft medical containers
- GPS, Wi-Fi and remote telemedical support
Customization
- Modular: operates independently or linked together as a field hospital
- Clinically versatile: primary care, laboratory (BSL 2/3), pharmacy, operating room, mental health, emergency care and more
Robust Design
- Self-sustaining: functions off grid or connected to local utilities
- Withstands heat, snow, rain and winds up to 116 MPH
- Climate-controlled, air purification systems & antimicrobial-treated surfaces
Award-Winning Solution

Global Programs is an awardee of the Ebola Grand Challenge granted by USAID, The White House Office of Science and Technology Policy, the Centers for Disease Control and the U.S. Department of State. From more than 1,600 applications, Global Programs is one of 12 winners selected.








