Matrix-Assisted Laser Desorption/Ionization Imaging Mass Spectrometry (MALDI-IMS) is a powerful analytical technique that enables spatially resolved molecular analysis of biological tissues. It creates detailed molecular maps of tissue sections, showing the spatial distribution of several classes of compounds, such as proteins, lipids, metabolites, and drugs.
The workflow for MALDI-IMS involves:
- Tissue Preparation:
- A thin tissue section (usually 10-16 µm thick) is mounted onto a specialized conductive glass slide (Indium Tin Oxide, ITO coated slides).
- A matrix, which is a light-absorbing organic compound, is uniformly applied over the tissue to aid in ionization. Several matrix types are available and selected according to the class of compounds investigated.
- Laser Desorption/Ionization:
- A pulsed UV laser excites the matrix molecules, which transfer energy to the analytes in the sample and ionize them.
- The ionized molecules are then introduced into the mass spectrometer.
- Mass Spectrometry Analysis
- The mass spectrometer measures the mass-to-charge ratio (m/z) of the ionized molecules.
- Each pixel in the image corresponds to a specific mass spectrum at that location.
- Image Reconstruction
- The collected mass spectral data are computationally processed to generate spatially resolved ion maps.
- These maps visualize the distribution of specific biomolecules across the tissue.
Advantages of MALDI-IMS:
- Label-Free: There is no need for antibodies or fluorescent tags.
- High Molecular Coverage: It can detect various biomolecules, including proteins, lipids, metabolites, and drugs.
- Spatial Resolution: It can achieve 5-10 µm resolutions, allowing subcellular imaging.
- Multiplexing: It can simultaneously detect hundreds of molecules in a single scan.
- Correlative Analysis: It can be integrated with histology and other imaging modalities, such as H&E staining and immunohistochemistry.
Applications for MALDI-IMS:
- Cancer Research: Identifying tumor biomarkers, studying drug penetration, and mapping tumor heterogeneity.
- Neuroscience: Investigating the distributions of lipids and neurotransmitters in the brain.
- Pharmacology: Tracking drug localization and metabolism in tissues.
- Metabolomics: Analyzing tissue-specific metabolic changes.
- Microbiology: Identifying bacterial colonies and their metabolites.
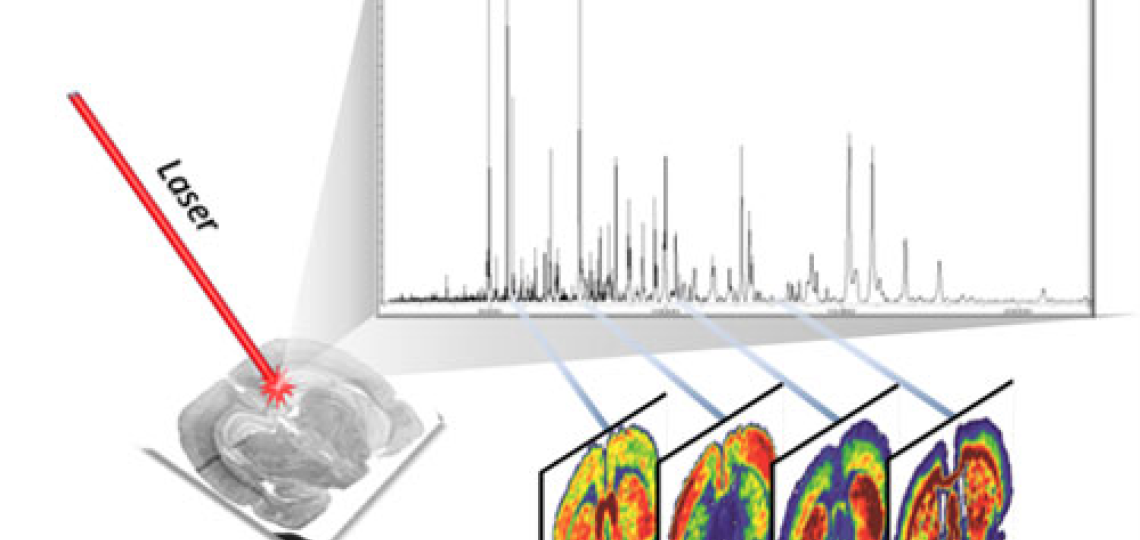
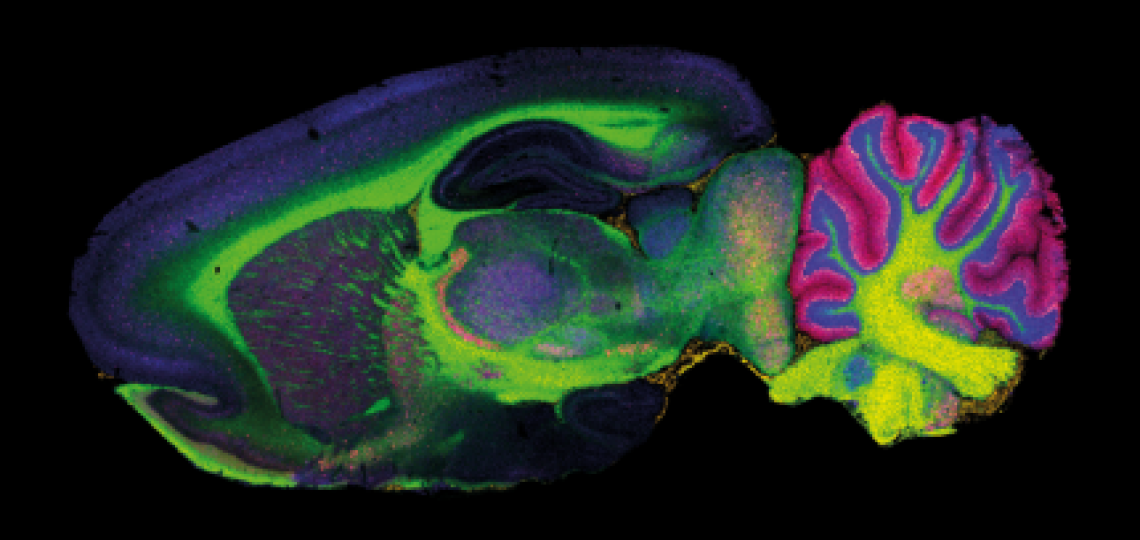
MALDI-IMS provides molecular insights with spatial resolution, making it an essential tool in biomedical research. Images from: https://www.bruker.com/en/applications/academia-life-science/imaging/maldi-imaging.html








