Most biological processes are facilitated by proteins. Herein, the 3D spatial arrangement of the protein active site and interaction regions are of paramount importance. In case there are no experimental structures available we use homology model structures to study the function and dynamics of our target proteins. We are also generating genome wide homology models of new microbial genomes with the goal of complementing sequence based functional annotation with structure based functional annotation (fig 3).
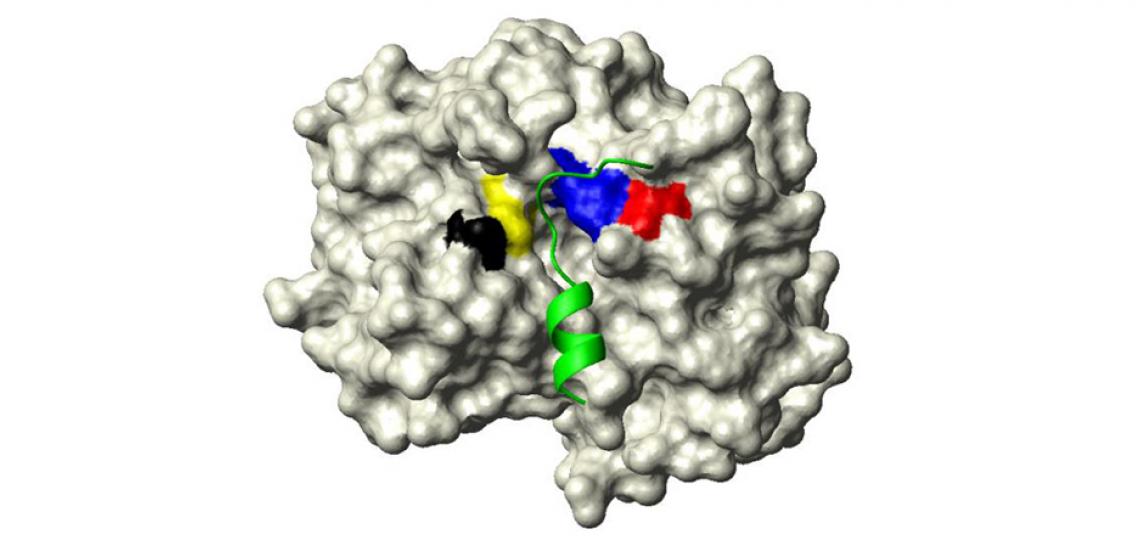
Fig 1: The active site of Clostridium difficile toxin B cysteine protease domain
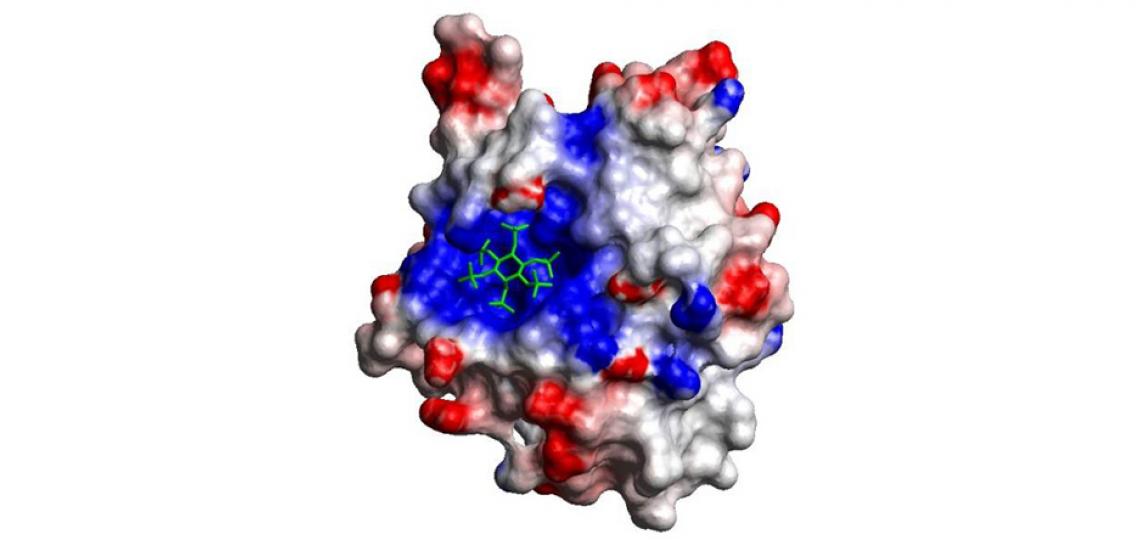
Fig 2: The electrostatic surface with its allosteric activator IP6 bound in a positively charged pocket.

Fig 3: Whole genome homology modeling








