Lung resection includes:
- Lobectomy - when one of the five lobes is removed;
- Segmentectomy - when a segment is removed;
- Wedge resection - when a small section of the lung is removed;
- Pneumonectomy - when an entire lung is removed. A complete lymph node dissection is also performed.
Why the Procedure Is Performed
Lung resection is indicated for the treatment of:
- Non-small cell lung cancer
- Metastasectomy for tumors that cannot be removed by lesser (sublobar) resections
- Carcinoid tumors that cannot be removed by lesser (sublobar) resections
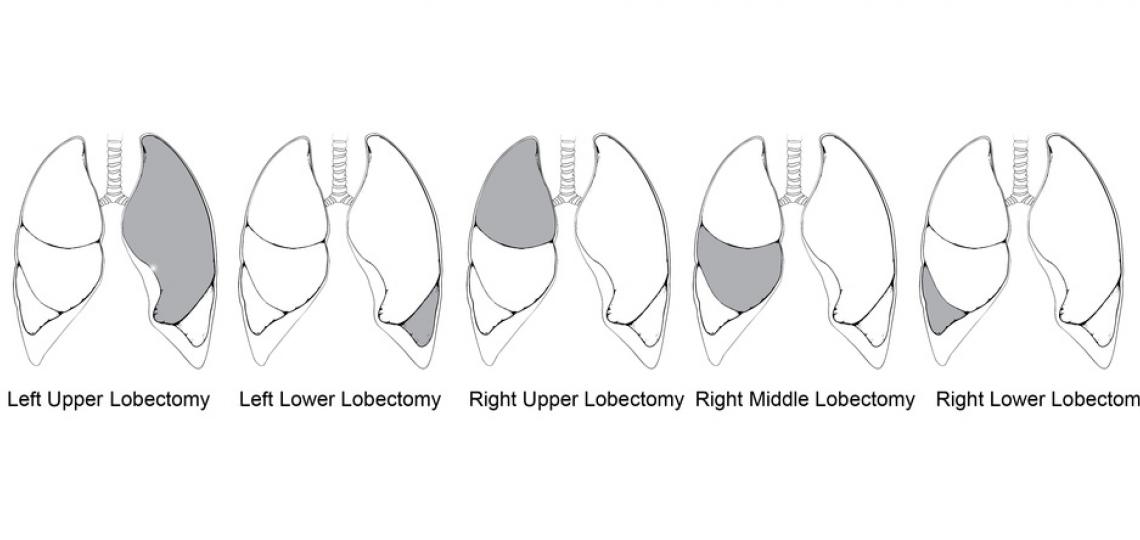
Lobectomy
A lobectomy is the surgical removal of one or more lobes of the lung. The other healthy lobes of the lung remain in the chest. There are five lobes or sections of the lung and five basic types of lobectomy named after the lobe of the lung being resected. Lobectomy is mainly indicated for the resection of malignant lung tumors such as lung cancer and carcinoid tumors. Lobectomy may be performed via an “open” or via a minimally invasive approach (VATS).
Types of Lobectomies
Grey indicates resected lobe
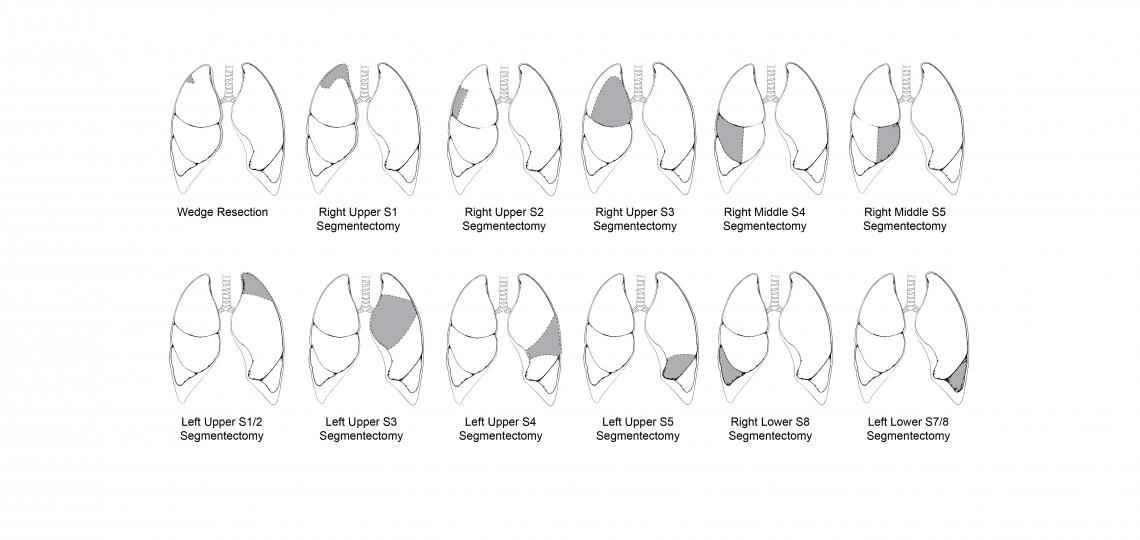
Segmentectomy and Wedge Resection
A wedge resection is performed to remove the cancerous cells along with a margin of healthy tissue surrounding the area. A segmentectomy is a larger segment of the lung but smaller than a lobe of the lung.
Types of Segment and Wedge Resections
Grey indicates resected area of the lung
Pneumonectomy
During a pneumonectomy an entire lung is removed when a smaller portion or lobe of the lung cannot be removed.








 Credit
Credit