Breast implant surgery for breast reconstruction
Breast implants are a way to recreate the shape of a breast after part or all of the breast is removed (mastectomy) because of cancer.
There are several types of implants that are available. Some of the most common implants have a soft silicone shell filled with saline (salt water) or silicone gel. Silicone may create a more natural-looking breast, because its weight and texture is more like breast tissue.
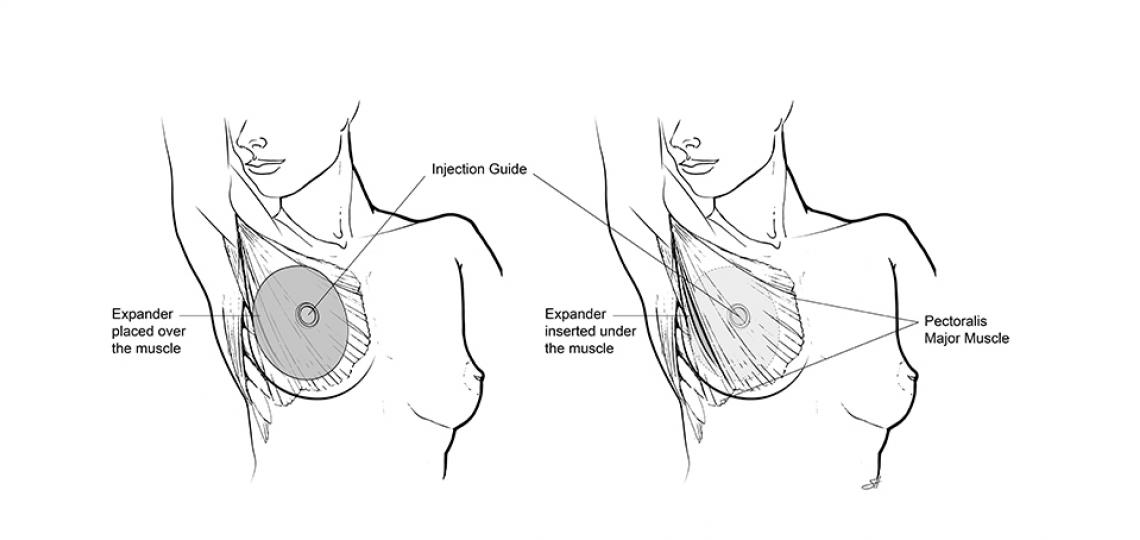
Breast reconstruction usually takes more than one surgery. Sometimes an implant is placed during the same surgery as mastectomy. But often the doctor will first place a tissue expander beneath the skin. Saline (or air) is added to the expander every 1 to 2 weeks to help stretch the skin. This may take several months. When the right size is reached, the expander is taken out and an implant is put in. The nipple and the darker area around it (areola) are created at a later time.
Implant surgery is done by a plastic surgeon. The breast surgeon who does your mastectomy can refer you to a plastic surgeon with special training in breast reconstruction.
You will meet with the plastic surgeon before your mastectomy to discuss the best procedure for you. He or she will be able to recommend the type of implant that will work best for your body type.
Before having this surgery or any other surgery, you may want to see another surgeon to get a second opinion.
A tissue expander can be inserted underneath or on top of the pectoral muscle on your chest.
Tissue flap surgery for breast reconstruction
Tissue flap surgery is a way to rebuild the shape of a breast using skin, fat, and possibly muscle from another part of the body. It is usually done after part or all of the breast is removed (mastectomy) because of cancer. It may also be done for women who have problems with breast development.
Breast reconstruction usually takes more than one surgery. The first surgery may be done during the same surgery as mastectomy, or it may be done later as a separate procedure. The nipple and the darker area around it (areola) are created at a later time.
Tissue flap surgery is done by a plastic surgeon. The breast surgeon who does your mastectomy can refer you to a plastic surgeon with special training in breast reconstruction.
You will meet with the plastic surgeon before your mastectomy to discuss the best procedure for you. He or she will be able to recommend the type of tissue flap surgery that will work best for your body type.
If you are not comfortable with the surgeon or the recommended treatment, you can see another surgeon to get a second opinion.
Types of Tissue Flap Surgery
Tissue flap surgery may be done in two ways:
"Pedicle flap" means the flap of tissue from the back or belly is moved to the chest without cutting its original blood supply. The tissue is pulled under the skin up to the chest area and attached."Free flap" means the tissue and blood vessels are cut. After the flap is in place, the surgeon sews the blood vessels in the flap to blood vessels in the chest area. This requires careful surgery by a surgeon who does microsurgery.
Here are some of the different types of tissue flap surgery, named for the area of the body where the tissue is taken.
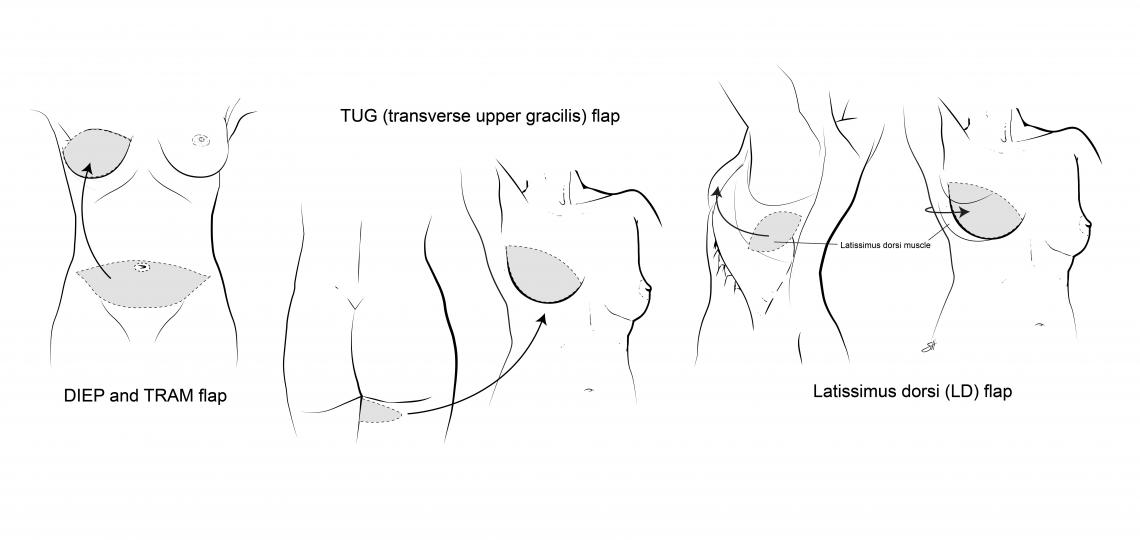
DIEP (deep inferior epigastric artery perforator) flap
DIEP (deep inferior epigastric artery perforator) flap is a free flap similar to TRAM. The surgeon takes fat and skin from the lower belly area but doesn't use the muscle. By saving the muscle, it helps avoid later belly weakness. Like TRAM, it results in a "tummy tuck."SIEA (superficial inferior epigastric artery) flap is similar to the DIEP flap. But with this surgery, the surgeon doesn't cut through the belly muscles to get the artery used for the new breast. Like DIEP, it results in a "tummy tuck."
Latissimus dorsi (LD) flap
Latissimus dorsi (LD) flap is a type of pedicle flap surgery. It uses muscle, fat, and skin from the upper back that is pulled under the skin to the chest area. The scar on the back can be placed at the bra line to make it less visible. Sometimes an implant is placed during the same surgery to make the breast larger.
TRAM (transverse rectus abdominis muscle) flap
TRAM (transverse rectus abdominis muscle) flap is one of the most common types of flap surgery. The surgeon takes muscle and tissue from the lower belly and moves it to the chest area. This reduces the amount of fat and skin in the lower belly and results in a "tummy tuck." TRAM may be done as either a pedicle flap or a free flap.
Gluteal free flap
Gluteal free flap is a free flap that uses muscle, fat, and skin from the buttocks to create a new breast. This may be a good choice for thin women who don't have enough belly tissue for DIEP or TRAM.
TUG (transverse upper gracilis) flap
TUG (transverse upper gracilis) flap is a free flap that uses tissue from the inner upper thigh to create a new breast. The scars are hidden inside the thigh and groin. Using the gracilis muscle from the thigh doesn't leave the leg weaker. This may be a good choice for a woman who has small breasts and little belly tissue.
Autologous Fat Transfer
Another type of breast reconstruction uses just fat to create a new breast. It is called autologous fat transfer or fat grafting. Unlike tissue flap surgery, this procedure uses liposuction to remove fat from your body (often from the belly or buttocks). Then the fat cells are injected into the chest wall to create a new breast mound.
© 2016-2019 Healthwise, Incorporated.








 Credit
Credit